This article is a the following regarding the “Sustainable Development in a Mega City I.“. This article connected to another article aka how to cool down cities in the future. In the previous article written about “Cool Down Cities: Innovative Solutions and White Surfaces“.
There are several answers how to cool down cities and green infrastructure is just one of them.
Green Infrastructure
Green infrastructure is a network of natural and semi-natural features and systems strategically planned, designed, and managed.
To provide environmental, social, and economic benefits within an urban or rural area.
Green Infrastructure Interactive Map
Maps can help us to know where and what we can find in cities regarding green infrastructure.
For example if we want to know more about Green Infrastructure Practices and about a Program Map in the City of New York here is a link to learn more about it.

Unlike traditional “gray infrastructure” (concrete structures & man-made systems), green infrastructure uses
- natural processes and
- vegetation to perform multiple functions,
often contributing to sustainable development and ecological conservation.
Greenfrastructures
The word define different green infrastructure (elements and systems) solutions, which create a network and make a city or their resident’s life greener.
There are several interconnected physical and digital elements can help in this.
Green Infrastructure examples
Urban Water Features
Water bodies like
- fountains,
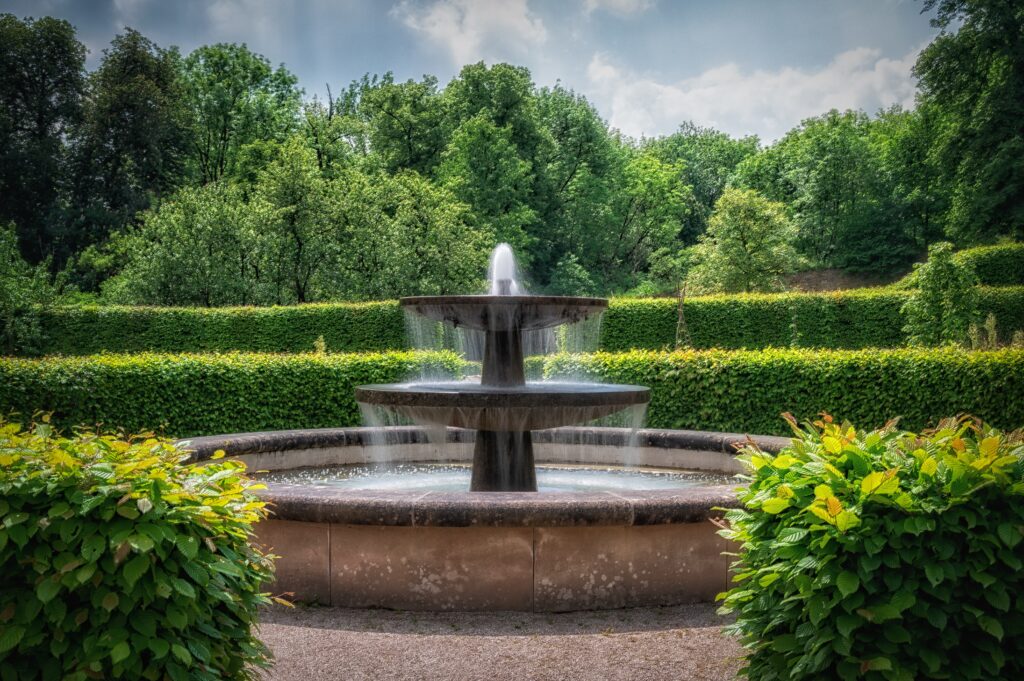

- ponds,
- artificial lakes,
which have a cooling effect through evaporation & help increase the overall greenery in the city.
In the design of those water bodies landscape architects will have more and more roles.
Sustainable Architecture
Encourage the construction of
- eco-friendly and
- energy-efficient buildings that reduce heat and incorporate green design elements.
Madrid Río Park
Madrid transformed the area along the Manzanares River into a green space called Madrid Río Park.
The project involved
- removing a highway,
- creating new parkland, and
- adding recreational areas, providing a cooler environment for residents.

Stormwater management
Portland’s Sustainable Stormwater Management
Portland, Oregon, employs green streets with
- bioswales &
- permeable pavements
to manage stormwater and reduce heat, contributing to the city’s sustainability goals.
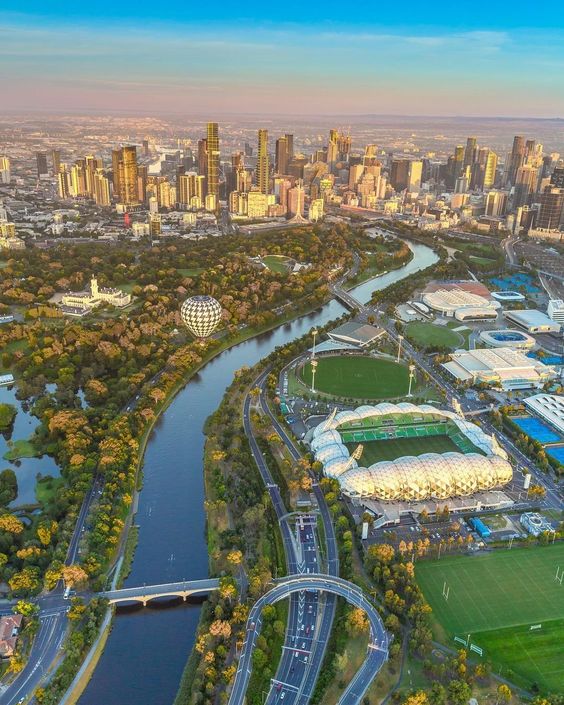
Urban Forest Strategy – Melbourne
Melbourne developed an Urban Forest Strategy to increase
- tree canopy cover,
- reduce heat stress, and
- improve the overall livability of the city.
The strategy involved:
- Increasing Tree Canopy Cover: planting new trees in various locations, including streets, parks, and public spaces.
- Diverse Tree Selection: selecting a diverse range of tree species to enhance biodiversity and ensure resilience against diseases and climate change impacts.
- Community Engagement: engaging the community in tree planting and maintenance programs to create a sense of ownership and responsibility among residents towards the urban forest.
- Greening of Public Spaces: creating green spaces and pocket parks.
- Cooling Effect and Heat Mitigation: planting trees strategically urban heat islands.
- Water Management: the strategy incorporated water-sensitive urban design principles.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: regular monitoring & evaluation of tree health and growth.
- Collaboration with Stakeholders: the success of the Urban Forest Strategy relied on collaboration.

Urban Forest – Madrid
Madrid actively working on expanding and promoting its urban forest, often referred to as the “Madrid Forest” or “Monte de El Pardo.”
Monte de El Pardo
This forest, located on the outskirts of Madrid, is one of the largest urban forests in the world. Covers around 16,000 hectares and plays a crucial role in maintaining the city’s environmental balance.
The forest contains a variety of plant and animal species and provides numerous recreational opportunities for residents and visitors.
The forest is easily accessible from the city center, making it a popular destination for residents and tourists alike. Visitors can reach it by public transportation or private vehicles.
Reforestation and Conservation
Madrid actively involved in reforestation efforts within the urban forest to combat deforestation and promote biodiversity. Various programs and initiatives have been implemented to protect and preserve this natural resource.
Recreational & Cultural Activities
The Madrid urban forest offers numerous recreational activities such as hiking, picnicking, cycling, and bird-watching. Many trails and paths have been established to facilitate outdoor exploration.
Educational and cultural programs and events held in the Madrid urban forest to raise awareness about its significance and promote environmental conservation.
Environmental Benefits
The forest helps improve air quality in Madrid by acting as a natural carbon sink and providing oxygen. It also plays a role in regulating temperature and reducing the urban heat island effect.
Sustainable Transportation
It is important to improve
- public transportation,
- cycling infrastructure, and
- pedestrian pathways
to reduce the reliance on private vehicles and lower emissions contributing to heat.
Copenhagen’s Bicycle-Friendly Infrastructure
As we all know Copenhagen invested heavily in creating
- an extensive network of cycling paths and
- pedestrian-friendly zones, reducing the use of cars and lowering heat emissions.
Creating greener cities
Urban Greening
Increase the number of trees, parks, and green spaces throughout the city. Green infrastructure like trees provide shade, absorb heat, and release moisture through transpiration, helping to cool the urban environment.
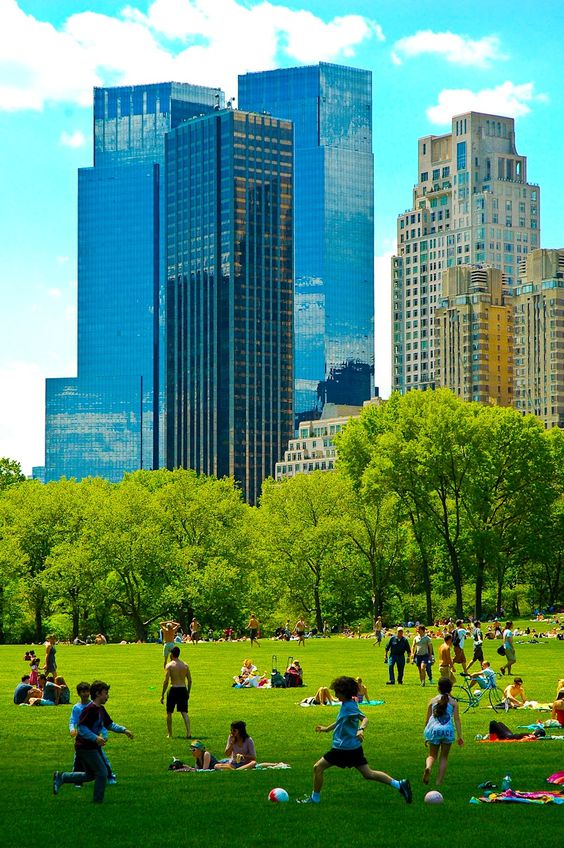
“Million Trees NYC” Project
This initiative aimed to plant one million new trees across New York City’s five boroughs. Trees were strategically planted in parks, streets, and public spaces to help cool the city and improve air quality.

Singapore’s “City in a Garden”
Singapore is renowned for its urban greening efforts.
The city has a comprehensive plan to create green spaces, rooftop gardens, and park connectors, maximizing the presence of plants and trees throughout the urban landscape.
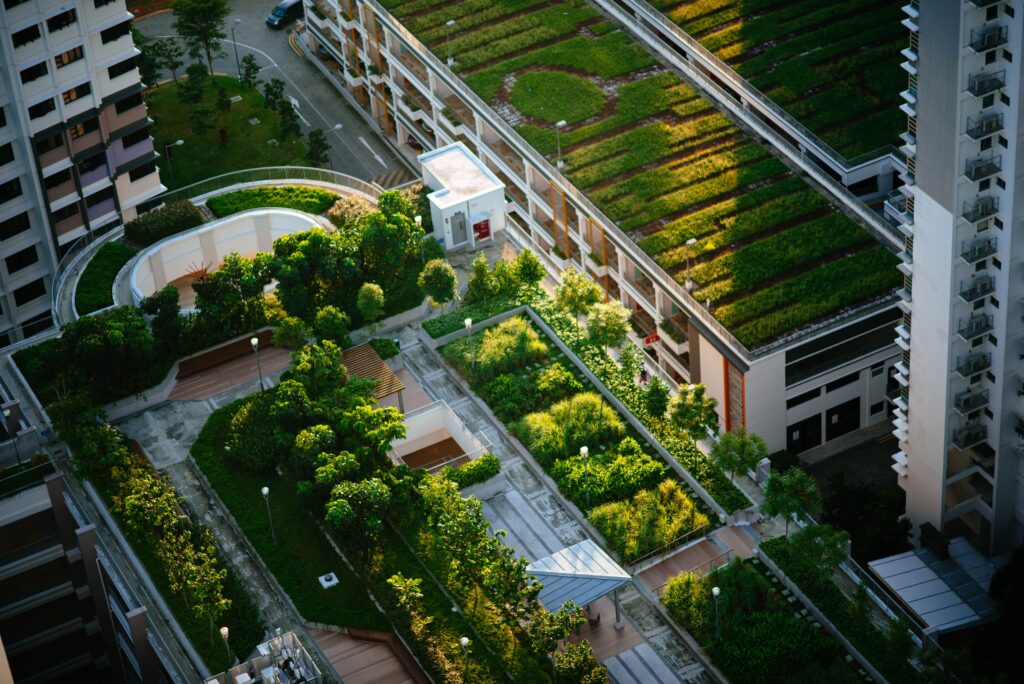

Green Roofs and Walls
Install green roofs and walls on buildings to add vegetation and create a cooling effect. These green surfaces help reduce the heat absorbed by buildings and improve air quality.
Tokyo’s Green Roofs and Walls
Tokyo embraced green roofs and walls in various buildings, including commercial spaces and residential complexes, to enhance the city’s greenery and reduce heat buildup.
For example Tokyo Plaza has Green roofs too.

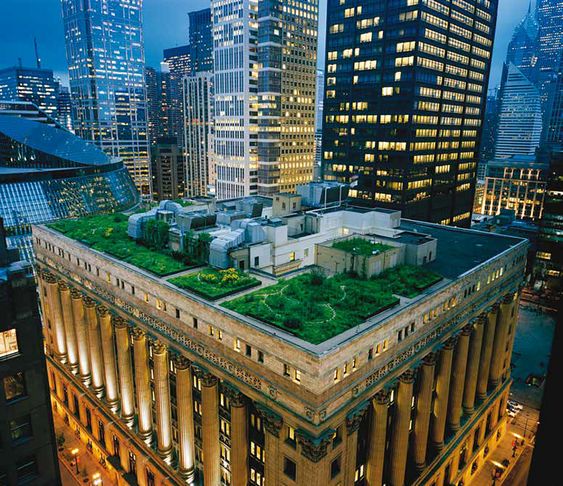
Chicago’s Green Roof Initiative
Chicago has been encouraging the construction of green roofs on buildings through incentives and regulations.
The Chicago City Hall is a famous example of a green roof that helps cool the building and the surrounding area.
Next to this aesthetically looking good too from outside.

Milan’s Bosco Verticale
The Bosco Verticale, or “Vertical Forest,” is a pair of residential towers in Milan, Italy.
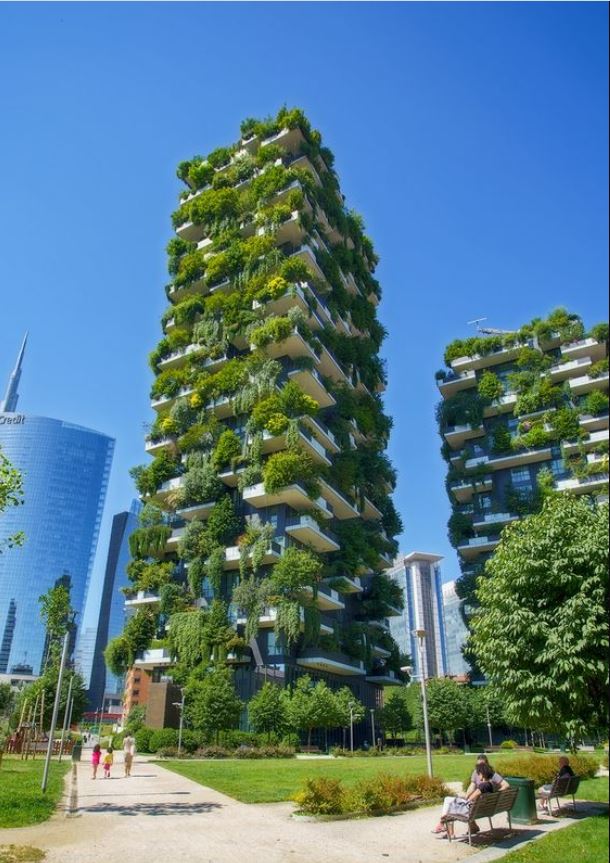

These towers are covered with more than 900 trees and over 20,000 plants.
It provides shade, absorbs CO2, and contributes to the city’s biodiversity.
Urban Agriculture
Promote
- rooftop gardens and
- community gardens
to enhance green spaces, grow food locally, and reduce the heat island effect.
Green Streets
Implementing green streets with bioswales and permeable pavements that manage stormwater and reduce heat.
Individual contributions
Urban Green Spaces
Encourage and participate in efforts to create and maintain parks, gardens, and green spaces within the city to promote natural cooling.
Advocate for Green Urban Planning
Engage with local authorities and advocate for urban planning policies that prioritize green infrastructure and sustainable practices.
Use Sustainable Transportation
- Green Fuels
- Electric Vehicles (EVs)
- Integrated Transport Systems
- Transportation Demand Management (TDM)
- Urban Planning for Transit-Oriented Development
Public Awareness and Education
Raising awareness among residents about the importance of creating urban green infrastructure and its impact on cooling the city is important. In addition to this combining strategies and collaboration of governments, businesses, and citizens, cities will become greener, more sustainable, and cooler places.
These all contibute to sustainable development & sustainability goals of the cities.
